How do I add an SPF record?
SPF or Sender Policy Framework is a published DNS record specifying domains or IP addresses authorized to send emails for a domain. Inbound emails that do not match the published SPF are spam. SPF records help authenticate the email sender against a list of authorized senders. This provides a safeguard against email spoofing.
The quantity of spam and level of sophistication in techniques used by spammers is increasing. Currently, 45% of all emails sent daily are spam, with some companies estimating the figure to be much higher (SpamLaws).
To combat nuisance & malicious emails, multiple layers of protection are in place, including SPF; which is becoming standard practice for mail. Some mail providers will automatically assign non-SPF custom domain emails to spam or junk folders. If you want to aid your overall email deliverability, you need an SPF record.
Table of Contents
- SPF Syntax
— 1. SPF Qualifiers.
— 2. SPF Mechanisms. - Add an SPF Record in cPanel
— 1. Email deliverability tool (easy).
— 2. Zone editor (advanced).
SPF Record Syntax
There are multiple ways to configure an SPF record. The easiest is using the suggested record provided or an SPF generator. By learning basic SPF record syntax, resolve SPF issues easily or add further configuration.
v=spf1 ip4:() include:192.168.0.1 +a +mx +ip include:servers.mail.net ~all
Example SPF Record
In the above example, “v=spf1″ denotes this TXT record as an SPF record. This is because a domain can hold multiple TXT records. The remaining part of the record consists of qualifiers and mechanisms.
SPF Qualifiers
Qualifiers determine the action taken for defined mechanisms.
- + Pass – An IP address matching a mechanism with this qualifier will pass an SPF check.
- – Fail – An IP address matching a mechanism with this qualifier will fail an SPF check.
- ~ Soft Fail – works similar to pass, but marks the mail for failing the SPF check.
- ? Neutral – SPF check will neither pass nor fail.
SPF Mechanisms
Mechanisms designate authorized outbound mailers for a domain.
- ip4 – Used to specify individual IPv4 addresses.
- include – Searches a domain for a corresponding record.
- a – Checks the sender IP against the listed A record
- mx – Checks published MX records.
- all – Denotes “always matches”.
Add an SPF record in cPanel
Our cPanel hosting provides two methods for adding a record. The easiest, most user-friendly way is through the email deliverability tool, which configures a “default” record. Because SPF is essentially a TXT DNS record, the zone editor tool can also be used.
Log in to cPanel and choose either of the following guides.
Email deliverability tool
- First, under the email section, click “email deliverability”. Because there are multiple themes or styles available, it may look different for you.
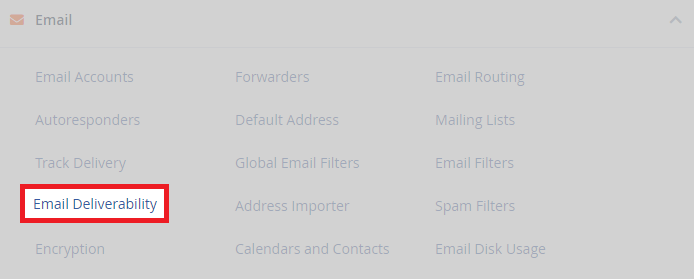
- Afterwards, in the tool, click on “manage” for the domain you want to add an SPF for.
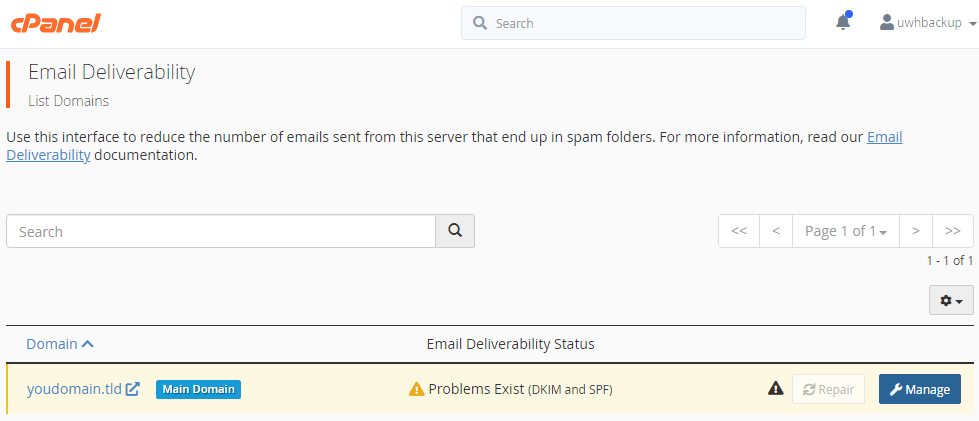
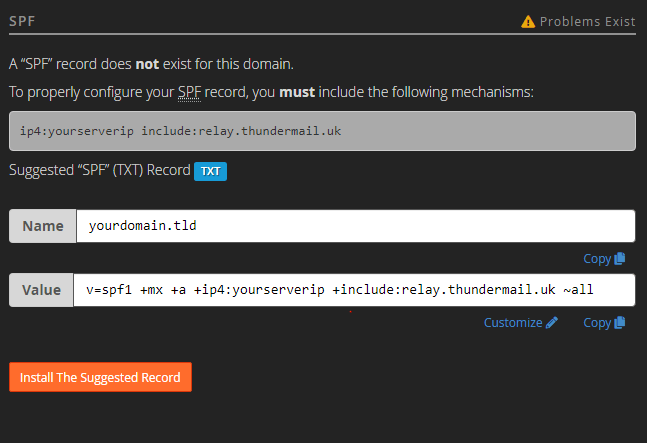
- Finally, scroll down to the SPF area. From here you can see the suggested record, if you need to customize this record then click “install the suggested record”.
Zone editor
- To add a record, scroll down in cPanel to the “domains” section and click on “zone editor”.
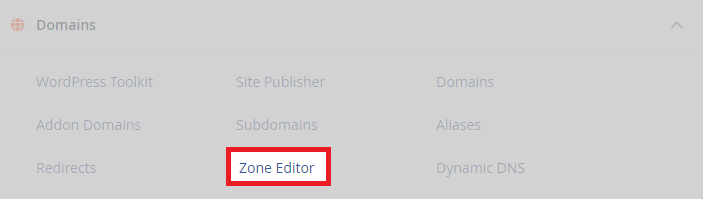
- From here, click the manage button which coincides with your domain.
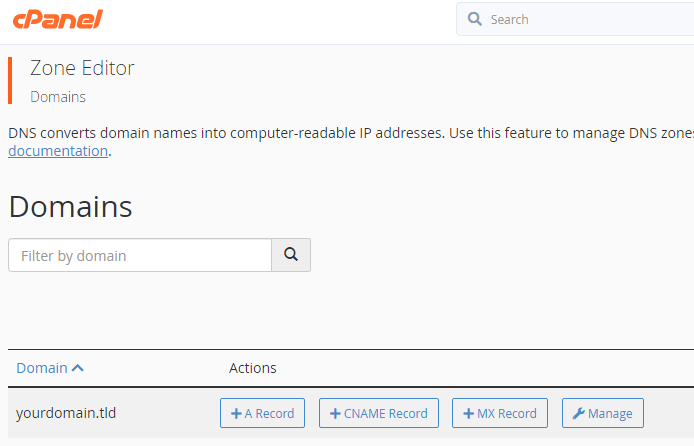
- Afterwards, on the zone records page. Click add record and change the type to TXT.
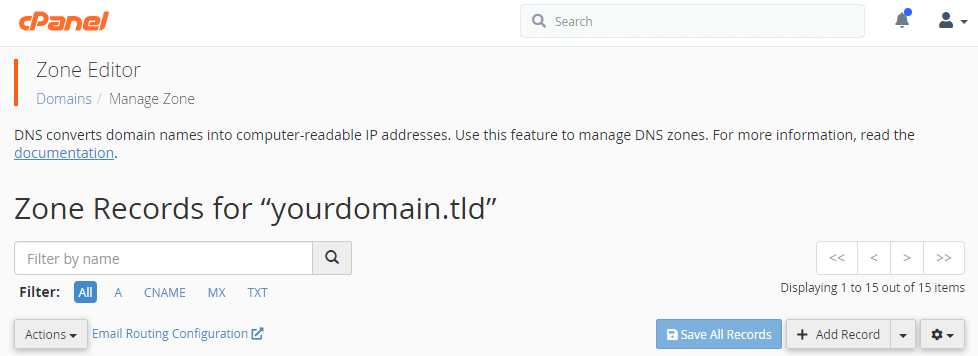
- Moving on, enter the domain name followed by a period (.). For example, if your domain is “yourdomain.tld” enter yourdomain.tld.
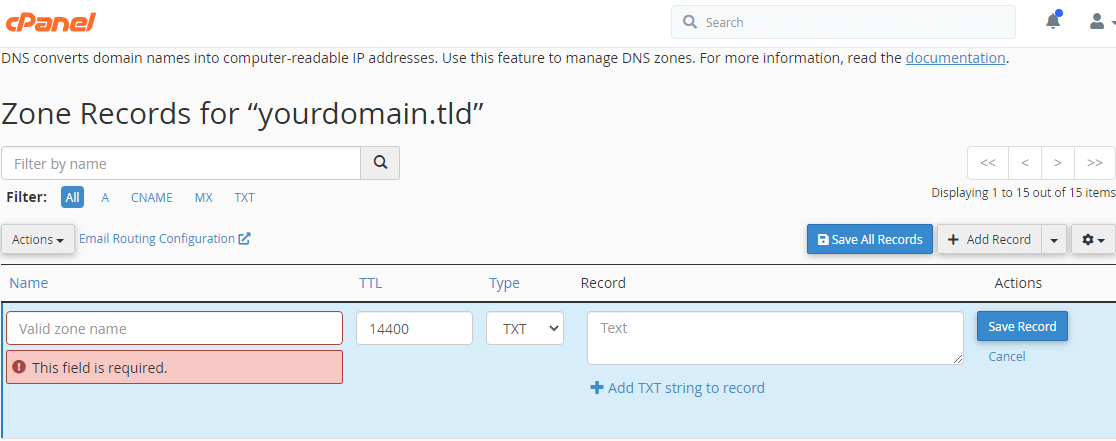
- Finally, add your SPF record. And click “save record”.